1590
Invention of the first compound microscope. This invention was attributed to Zacharias Janssen, however this claim has been the subject of much dispute and was possibly fabricated by his son following his death.
1665
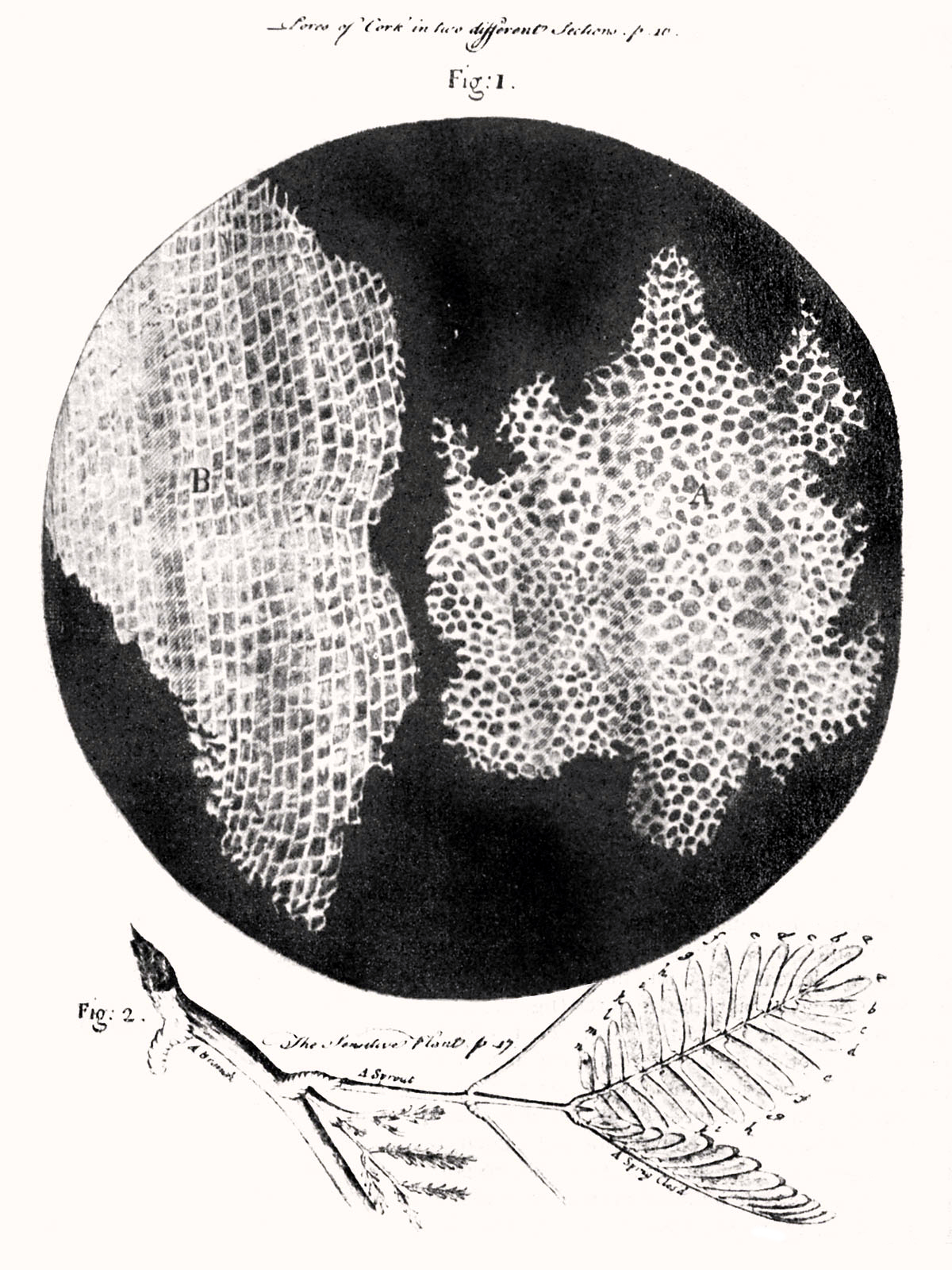
Robert Hooke observed cork cells under the microscope.
He coined the term "cells" as the plant cells he observed reminded him of the cells that make up honeycomb.
His ideas were published in the book Micrographia. This was the first book to include illustrations of insects and plants as seen through microscopes.
1674
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first person to observe living cells under the microscope while examining algae Spirogyra.
Starting from the assumption that life and motility are similar he concluded in his dairy that the moving objects he saw were little animals.
His interest in lens-making allowed him develop lenses of higher magnification allowing him to later observe protozoa, red blood cells and spermatozoa.
1831
Robert Brown observed an opaque area while studying orchid cells under the microscope, he called it the "nucleus". Although the nucleus had been described previously this was the first time it was given a name.
1838
Cell theory is proposed by plant scientist Matthias Schleide and physiologist Theodor Schwann.
In 1838 Schwann published his cell theory stating that:
1. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure, physiology, and organisation in living things.
2. The cell retains a dual existence as a distinct entity and a building block in the construction of organisms.
It also incorrectly stated that cells arise from spontaneous generation.
1857
Albert von Kölliker recorded the first observation of mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell. He noticed arrangements of granules within the human muscle cells he was studying. The granules he observed would not be termed mitochondria until many years later in 1898.
1858
Rudolf Virchow contributes to cell theory stating that “All cells only arise from pre-existing cells”.
He was heavily influenced by the work of Robert Remak, who had demonstrated that the origin of cells was by the division of pre-existing cells. He published Remak's work under his own name leading to a falling-out between them.
1878
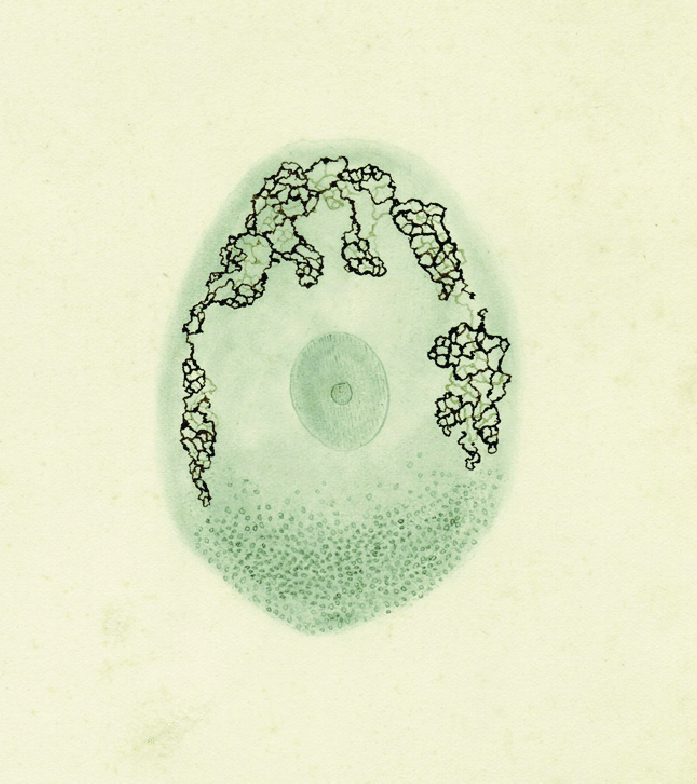
Walther Flemming observes the behaviour of chromosomes while investigating the process of cell division. He noted that "the nucleus always splits before the cell does" and coined the name mitosis to describe the process of cell division that results in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells.
1898
Camillo Golgi is the first to identify the Golgi apparatus using new staining techniques. The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing and packaging proteins and lipids for export from the cell. Unfortunately at the time his discovery was largely rejected by other scientists and only become established at a later date upon the invention of the electron microscope.
To be continued...
Unfortunately it took me longer than expected to make this page and I didn't quite manage to finish it in time for the event! However I have really enjoyed researching this topic and will definitely be adding more to this page in the future :)